How is AI Affecting Sino-American Relations?
China and the US are contending their respective technological supremacy in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) – in turn, this fight for technological hegemony will affect Sino-American relations, and the world.
If there is anything I want to do before I die, it is to go to China. If I don’t, I want my children to.
– President Richard Nixon, October 5, 1970.
After his election in 1968, Richard M. Nixon was the first U.S. president to visit the People’s Republic of China since its foundation in 1949. The visit represented a new development in Sino-American relations because, despite their historical hostility, the two countries established strong bilateral relations.
In fact, Richard Nixon’s opening to China occurred in 1971, when National Security Advisor and future Secretary of State Henry Kissinger took two trips to China – the first made in secret – to negotiate Sino-American rapprochement with Premier Zhou Enlai.
After more than two decades of unfriendly relations, Nixon dramatically changed U.S. diplomatic history with his trip to China on February 21-28, 1972
Notoriously, China has always represented an important target for America’s interests, especially for its market and its strategic position in Asia, and these reasons have always implied America’s long-lasting connection with China for more than two centuries.
China became inevitably linked to the development of America’s national destiny through the far-reaching expeditions of the Nineteenth century.
China came to be seen by the United States as the eastern extremity, the antipode to Europe for its culture, language, arts, philosophies and beliefs, an alternative to the West for its majesty.
The economic motive constituted another good reason for the United States to make China a target of America’s Manifest Destiny, becoming an important object of expeditions and ambitions; and, in the Nineteenth century, many Americans conceived the importance of trade with China as America’s Manifest Destiny.
Consequently, the beginning of new, positive relations between the United States and China in 1972 has initiated a process of mutual accommodation.
This mutual accommodation was especially evident in the general principles agreed upon between China and the United States, on February 28, 1972, in Shanghai, when President Nixon and Chairman Mao Zedong of the Communist Party of China agreed that peace in Asia and in the world required efforts from both sides in order to reduce immediate tensions.
Thus, progress toward the normalization of relations was in the interests of all countries because both countries wished to reduce the danger of international military conflict without seeking hegemony in the Asia-Pacific region.
As a result of the Shanghai Communiqué, the major achievement was the Sino-American rapprochement during the Nixon administration. The rapprochement, in turn, paved the way for the current economic interdependence between the United States and China.
Nixon’s considerable contribution to the opening to China has exerted a major influence in the following presidential administrations, while revolutionizing American foreign policy.
Nixon’s opening to China in 1972 launched a new path for American foreign policy and Sino-American relations, which was destined to go beyond the Cold War period
In fact, today, the United States and China face many challenges because of the rapid globalization and growing strategic interdependence between the two countries, which are now not only economically but also technologically intertwined.
One of the major challenges that Sino-American relations are now facing concerns their respective breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, namely AI.
Artificial intelligence has gone from futuristic speculation to present-day reality. Today many machine learning systems have already been developed for commercial use. The applications are tremendously varied, and adoption is growing rapidly in sectors such as finance, health care, and manufacturing.”
The concept of artificial intelligence is generally referred to the idea that computer systems can now perform functions typically associated with the human mind.
This evolution is especially the result of improvement and achievement in data collection and aggregation, algorithms and processing power.

According to a McKinsey Global Institute report:
Where computer systems once had to be programmed to execute rigidly defined tasks, they can now be given a generalized strategy for learning, enabling them to adapt to new data inputs without being explicitly reprogrammed.”
AI capabilities are essential because of their ever-growing potential to foster human welfare, live, education and environment. In fact, the fields of application of artificial intelligence cover several areas: from medicine to commerce, from education to environmental protection.
Nevertheless, there are also secondary problems that should not be overlooked, such as the importance of safeguarding complex ethical, legal, and security questions.
AI may raise surrounding issues such as privacy, discrimination, liability, and regulation.
Moreover, AI’s impact can be crucial when considering Sino-American relations.
The two most important nations in the world are, in fact, confronting and fighting each other in the realm of artificial intelligence, which is now the new priority in seeking world dominance and appeal.
In particular, China is investing huge financial resources in R&D, becoming one of the most important global hubs for the development of artificial intelligence.

China can benefit from its vast population and variety of industries by building a more competitive innovation capacity. This achievement may lead China to catch the United States out in AI research, innovations and startups.
Specifically, China’s future economic growth could soar by significant AI’s effects on productivity, especially by developing a competitive innovation capacity as the population ages.
According to the McKinsey Global Institute report:
AI-led automation can give the Chinese economy a productivity injection that would add 0.8 to 1.4 percentage points to GDP growth annually, depending on the speed of adoption.”
As for Sino-American relations, there is a high probability that technological advancement in the field of artificial intelligence could lead to strong competition between the United States and China.
AI may emphasize both massive rivalry on the U.S.-China relationship as well as hope for potential collaboration.
Recently, under President Trump, power competition has become the major principle of American foreign policy. His “America First” slogan has been the echo for the twenty-first century American nationalism based on a key issue: regain to America its worldwide leadership.
Trump’s campaign created a strong public appeal focusing on extremely upsetting issues such as economic and industrial recovery; illegal immigration; unemployment; increasing terrorism; disadvantageous international trade agreements; middle-class taxation; weak foreign policy and, eventually, the unfair China.
As Trump stated in one tweet on July 2017:
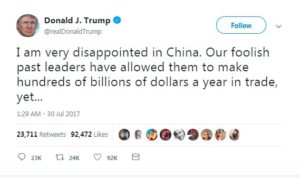
Trump’s massive disappointment with China was and is mainly focused on four pillars: China’s continuous economic and financial integration within the international system; its increasing forceful attitude in the South China Sea; its growing military expenditures, and the fact that all these factors were detrimental to the United States’ global balance of power.
In some ways, this competing attitude can be described as a Cold War echo in terms of the bilateral, technological opposition between the United States and China.
When compared to the Cold War period, some analogies can be found in the so-called “arms race” rivalry, which opposed the United State and China in the competition for advanced technology of the time.
Today, the same narrative can be found in the escalating competition between the United States and China in terms of innovative capacity. AI is exacerbating the Sino-American rivalry, leading to the intensification of sticky issues such as the opposition between liberal democracy and authoritarian capitalism.
China and the US are contending their respective technological supremacy in the field of artificial intelligence and, in turn, this fight for technological hegemony is affecting the stability of Sino-American relations, and the world
Moreover, AI is driving both countries to excel ahead of the rest of the world in terms of economic growth, modernization and long-term national power.
As a result, competition in the field of advanced technologies is accelerating the incidence of the historical rivalry between a Western and an Eastern model, with possible implications for the stability of the international system.
In turn, the adoption of advanced technologies may contribute to intensify the incidence of extreme societal disruptions in both countries.
Having said that, it is possible that this bilateral opposition in the field of artificial intelligence will end up creating enormous stress in Sino-American relations in the medium-long period.
In this respect, it would be desirable for the world’s governments to work together in order to find a compromise. In particular, the European Union should collaborate with leading countries by playing the role of mediator in this new, historical development that risks compromising the future of the international system.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Cover image, pictures and video used under CC BY 2.0
Video: America’s AI War with China from BEME News
Read other stories by Roberta Meloni.